Obstetrics and Gynecology in Turkey
Obstetrics and gynecology in Turkey play an important role in the country’s healthcare system. Turkey has state-of-the-art medical facilities, qualified professionals and a variety of treatment options for women at all stages of life, from adolescence to adulthood and beyond.
Genital aesthetics
Genital aesthetics refers to medical procedures aimed at improving the aesthetic appearance of the female genital region. This can be done through various surgical and non-surgical methods, depending on the needs and wishes of the patient. The most common procedures include labiaplasty (reduction or reshaping of the labia), vaginal tightening, labia augmentation, clitoris hood reduction and G-spot augmentation. These procedures can be performed for aesthetic or functional reasons and are intended to increase the self-confidence and well-being of the patient.

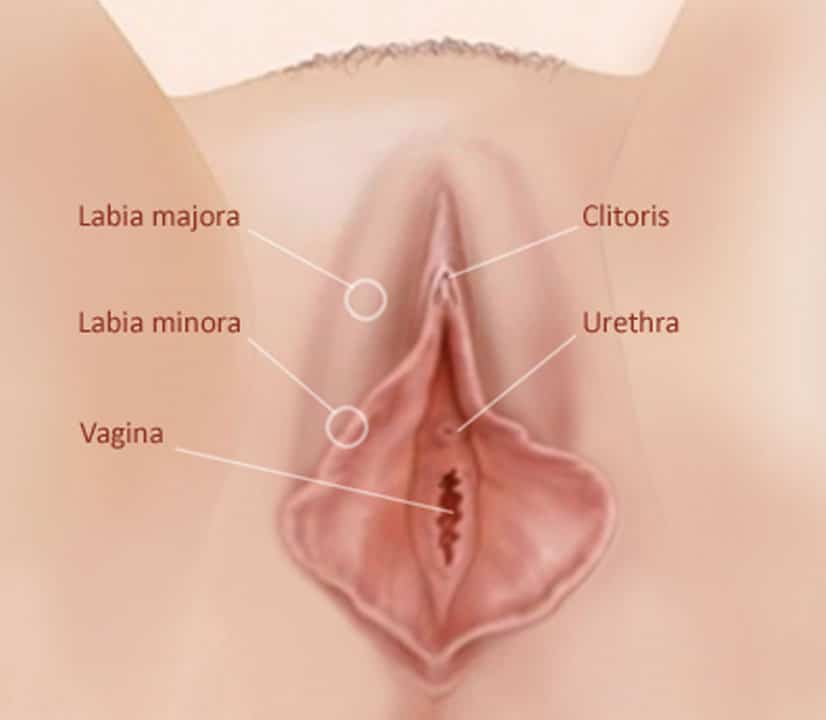

Cosmetic Gynecology
Cosmetic gynecology encompasses a variety of treatments and procedures aimed at improving the appearance and function of the female genitalia. This includes not only aesthetic procedures such as genital aesthetics, but also non-surgical treatments such as laser therapy for skin tightening or rejuvenation of the vaginal region, hyaluronic acid injections to improve vaginal moisture and external genitalia, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments to increase sexual function and desire.
Vaginismus
Vaginismus is a condition in which the muscles around the vagina contract unconsciously and uncontrollably, which can make sexual intercourse, gynecological examinations, or the insertion of tampons or menstrual cups painful or impossible. Treatment for vaginismus may include a combination of physiotherapy exercises to relax the pelvic floor muscles, psychotherapeutic interventions to deal with anxiety and trauma, as well as gynecological consultations and drug therapy if necessary. An individual approach is important to find the best treatment for each patient.
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex medical process that involves several steps, from the initial consultation to discharge. Here are the typical steps in the IVF process:
1. Initial consultation and examinations
The IVF process begins with an initial consultation with a reproductive medicine specialist. During this consultation, the couple’s or woman’s medical history is taken and a thorough examination is performed to determine if IVF is a suitable treatment option. This may include blood tests, ultrasound scans and other diagnostic procedures.


2. Treatment planning
After the initial consultation, the doctor will create an individualized treatment plan for the couple or woman based on their specific needs and the cause of infertility. This plan may include medications to stimulate the ovaries, cycle monitoring, ultrasound scans and blood tests.
Treatment process
3. Stimulation of the ovaries
The next step in the IVF process is to stimulate the woman’s ovaries with hormones to increase egg production. This is usually done through injections of hormones over a period of about ten to twelve days. During this time, the woman is monitored regularly to monitor the progress of egg maturation.
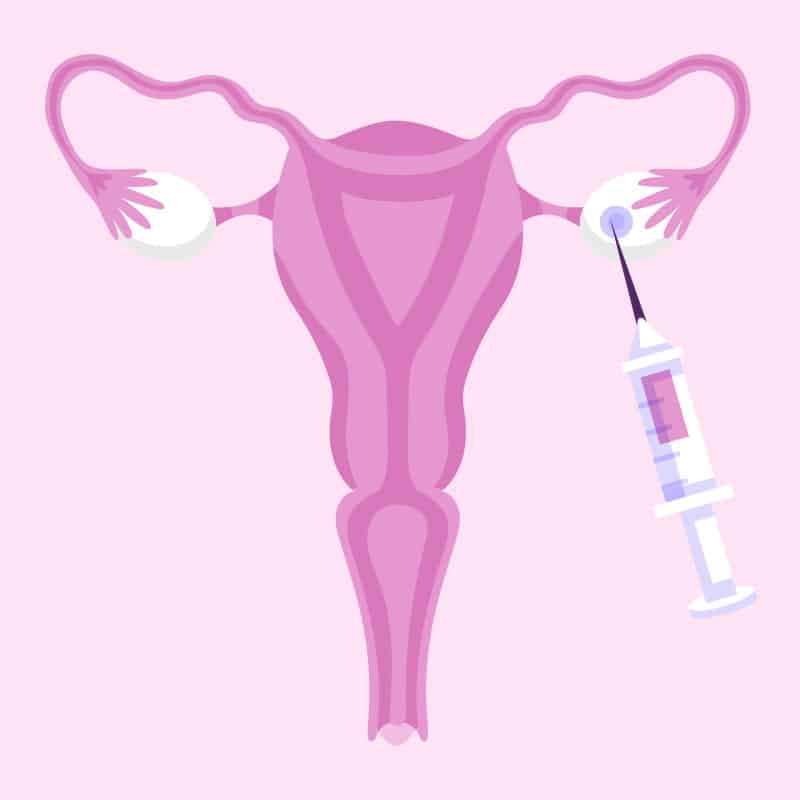
4. Egg retrieval (follicular puncture)
Once the ovaries have been sufficiently stimulated and the eggs are mature, egg retrieval is performed. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia and ultrasound guidance and involves removing the eggs from the ovaries with a thin needle.

5. Fertilization
After egg retrieval, the eggs are fertilized in the laboratory with the partner’s or a donor’s sperm. Fertilization can be done through conventional IVF, in which the eggs and sperm are placed together in a Petri dish, or through intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in which a single sperm is injected directly into the egg.

6. Embryo culture
The fertilized eggs are cultured and monitored in the laboratory to track their growth. Typically, the embryos are cultured in the incubator for about three to five days before being prepared for transfer.
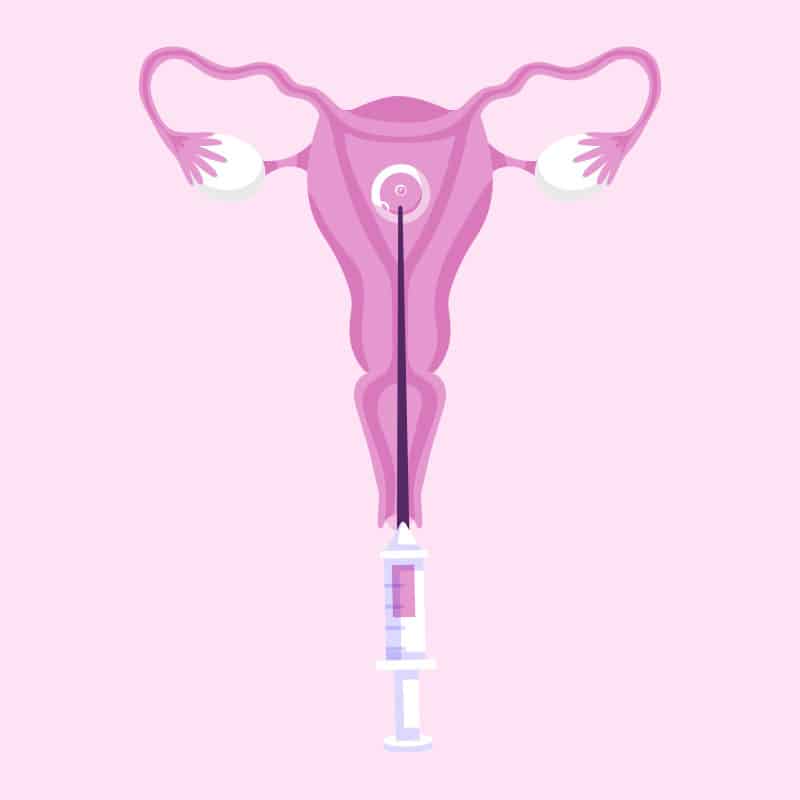
7. Embryo transfer
After culture, one or more embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus. This step usually occurs two to five days after egg retrieval and is done by inserting a thin catheter through the cervix.

8. Pregnancy and discharge
Approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is performed to determine whether the treatment was successful and pregnancy has occurred.
Pregnancy and discharge: If pregnancy is confirmed, the woman will be referred to her gynecologist for further care. If pregnancy does not occur, the IVF process may be repeated, depending on the couple’s individual circumstances.
The exact steps and progression of the IVF process may vary depending on the couple’s specific needs and medical condition. It is important that the couple or woman work closely with their doctor throughout the process and follow all instructions and recommendations to achieve the best possible results.